Coats JG, Maktabi B, Abou-Dahech MS, Baki G. Blue light protection, part II-Ingredients and performance testing methods. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021 Mar;20(3)
Mercurio DG, Wagemaker TA, Alves VM, Benevenuto CG, Gaspar LR, Maia Campos PM. In vivo photoprotective effects of cosmetic formulations containing UV filters, vitamins, Ginkgo biloba and red algae extracts. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2015 Dec;153
Burke KE. Interaction of Vit C and E as better Cosmeseuticals. Dermatol Ther. 2007;20:314–9.
Pinnell SR, Yang HS, Omar M, Riviere NM, DeBuys HV, Walker LC. Topical L ascorbic acid percutanous absorbtion studies. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27:137–42
Shanmugam S, Song CK, Kim DD, Choi HG, Yong CS, et al. Skin penetration and retension of LAA2PO4 using multilamellar vesicles. Arch Pharma Res. 2008;31:1652–8
Talakoub L, Neuhaus IM, Yu SS. Cosmeceuticals. In: Alam M, Gladstone HB, Tung RC, editors. Cosmetic dermatology. Vol. 1. Requisites in Dermatology. 1st ed. Gurgaon: Saunders Elsevier; 2009.
Niki E, Traber MG. A history of vitamin E. Ann Nutr Metab. 2012;61(3)
Alberts DS, Goldman R, Xu MJ, Dorr RT, Quinn J, Welch K, Guillen-Rodriguez J, Aickin M, Peng YM, Loescher L, Gensler H. Disposition and metabolism of topically administered alpha-tocopherol acetate: a common ingredient of commercially available sunscreens and cosmetics. Nutr Cancer. 1996;26(2)
Oomah BD, Ladet S, Godfrey DV, Girard B, Liang J, Characteristics of raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.) seed oil, Food Chemistry, 200, 69, 2
Ramadan MF, Fruit Oils: Chemistry and Functionality, Springer, 2019
Michalak M, Kiełtyka-Dadasiewicz A, Oils from fruit seeds and their dietetic and cosmetic significance, 2019, Herba Polonica, 64, 4
Park J-E, Kim HJ, Kim S-N, Kang SH, Kim YJ, Inhibitory Effect of Rosa multiflora hip Extract on UVB-induced Skin Photoaging in Hs68 Fibroblasts, 2015
Valerón-Almazán P, Gómez-Duaso AJ, Santana-Molina N, Bello MAG, Carretero G, Evolution of Post-Surgical Scars Treated with Pure Rosehip Seed Oil, Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications, 2015
Zhang Changcheng;Wu Degang;Wang Jingping;et al.(Institute of Botany,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing), Studies on the Chemical Constituents of Flannel Mullein (Verbascum thapsus), 《Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs》 1996-05
KK Kogje, VK Jagdale, SS Dudhe, G Phanikumar and RS Badere, Antioxidant property and phenolic compounds of few important plants from trans-himalayan regions of north india, Journal of Herbal Medicine and Toxicology 4 (2) 145-151 (2010)
F. X. Cunningham, Jr. and E. Gantt, “Genes and enzymes of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants”, Annu. Rev., Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998. 49
Harold C. Furr and Richard M. Clark, “Intestinal absorption and tissue distribution of carotenoids”, Nutritional Biochemistry 1997. 8
Michelangelo La Placa, Massimiliano Pazzaglia, Antonella Tosti, “Lycopenaemia”, JEADV 2000. 14
Devanand L. Luthriaa, Sudarsan Mukhopadhyaya, Donald T. Krizek, “Content of total phenolics and phenolic acids in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) fruits as influenced by cultivar and solar UV radiation”, Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2006. 19
Zsuzsanna Fazekas, Dayuan Gao, Rao N. Saladi, Yuhun Lu, Mark Lebwhol and Huachen Wei, “Protective effect of lycopene against ultraviolet B-induced Photodamage”, Nutrition and Cancer, 2003. 47(2)
Wilhelm Stahl, Ulrike Heinrich, Sheila Wiseman,Olaf Eichler, Helmut Sies and Hagen Tronnier, “Dietary Tomato Paste Protects against Ultraviolet Light–Induced Erythema in Humans” The journal of nutrition 2001.
A.V. Rao, L.G. Rao, “Carotenoids and human health” Pharmacological Research 55 (2007).
Giampapa et al, Topical composition for skin treatment to reduce lines and wrinkles of the face and body using a dual dna repair mechanism to address damage caused by aging and ultra – violet induced damage to the skin with combination of skin turgor enhancement compounds, Patent No . : US 9 , 968
Giulia Pastorino, Carla Marchetti, Barbara Borghesi, Laura Cornara, Stefaniа Ribulla, Bruno Burlando, Biological activities of the legume crops Melilotus officinalis and Lespedeza capitata for skin care and pharmaceutical applications, Industrial Crops and Products, Volume 96, February 2017
KOJO ESHUN & QIAN HE (2004) Aloe Vera: A Valuable Ingredient for the Food, Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Industries—A Review, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 44:2, 91-96
Cioca et al., Method Of Enhancing Biological Activity Of Plant Extracts Patent Application Publication (10) Pub.
Darr D, Dunston S, Faust H, Pinnell S. Effectiveness of antioxidants (vitamin C and E) with and without sunscreens as topical photoprotectants. Acta Derm Venereol. 1996 Jul;76(4)
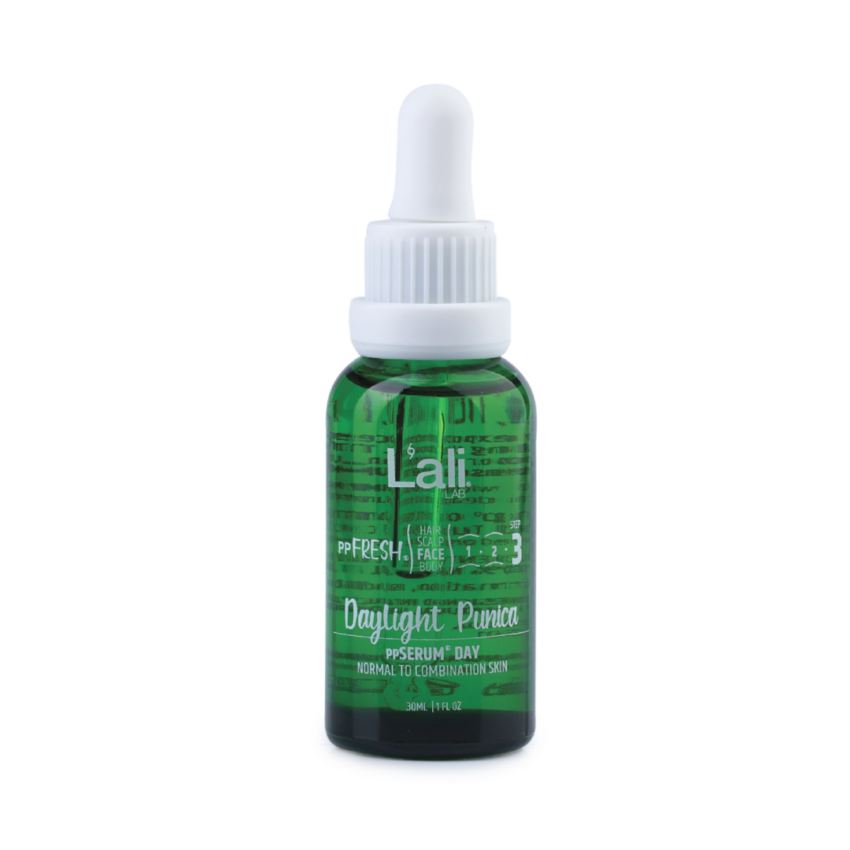 ДНЕВЕН СЕРУМ ЗА ЛИЦЕ | Daylight Punica | 30мл
2 × 32,79 € / 64,13 лв.
ДНЕВЕН СЕРУМ ЗА ЛИЦЕ | Daylight Punica | 30мл
2 × 32,79 € / 64,13 лв.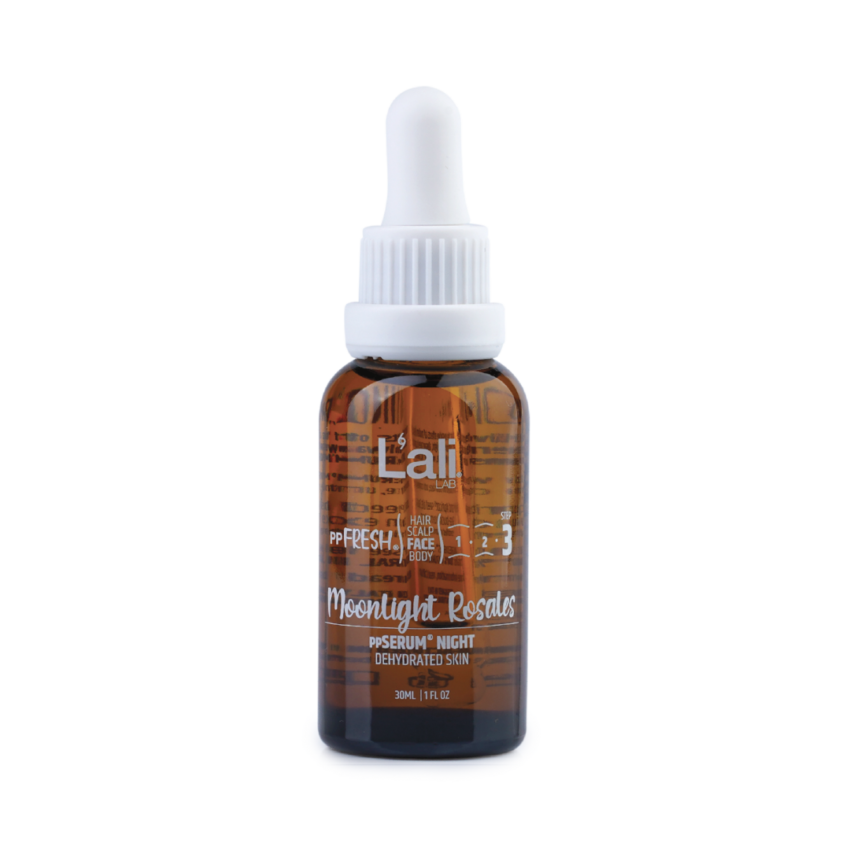 НОЩЕН СЕРУМ ЗА ЛИЦЕ | Moonlit Rosales | 30мл
1 × 34,84 € / 68,14 лв.
НОЩЕН СЕРУМ ЗА ЛИЦЕ | Moonlit Rosales | 30мл
1 × 34,84 € / 68,14 лв.